Information Fusion using LLMs
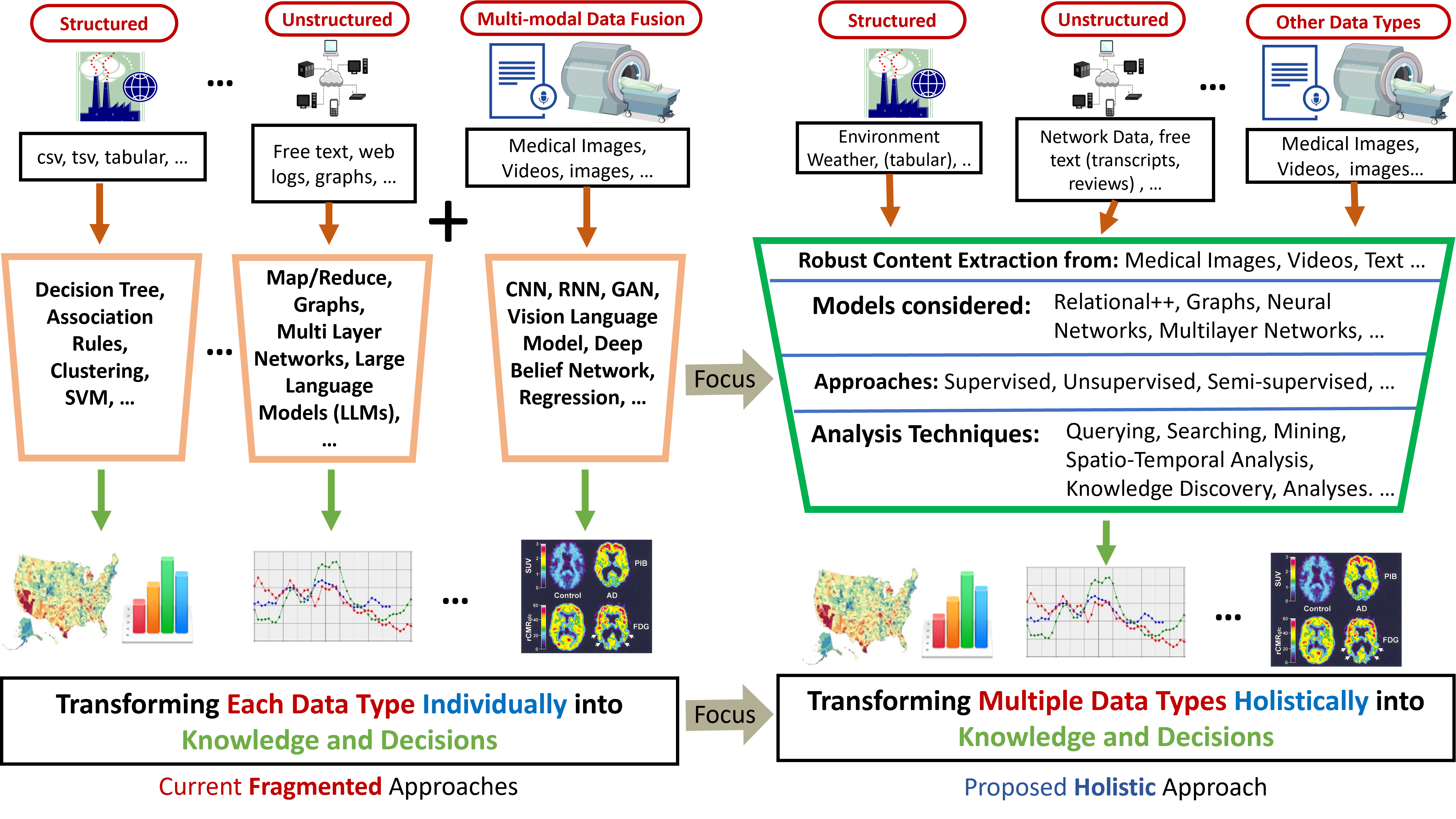
Before we can fully address data analytics and data science in all their breadth - especially aspects like velocity and veracity - we must first tackle the challenges of modeling large, diverse datasets (variety) and ensuring scalable processing (volume). Much of the existing work has focused on analyzing individual data types in isolation, such as structured transactional data, streaming data, text and natural language, images, videos, and others. However, when multiple heterogeneous data types must be analyzed together, entirely new challenges arise.
Previous efforts in areas like multisensor data fusion and multimodal deep learning address pieces of the problem but remain limited in scope. As our research, we are aiming to build a unified, general-purpose framework that supports:
- Converting diverse input data types into a canonical representation (including data extraction when necessary)
- Modeling the integrated data using concrete models, often through an intermediate abstraction such as extended entity-relationship diagrams
- Expressing analytical objectives in natural language and translating them into computable operations on the chosen model
- Designing efficient algorithms for analysis, inference, and knowledge discovery
- Drilling down into and visualizing results in ways that remain tied back to the original application data.